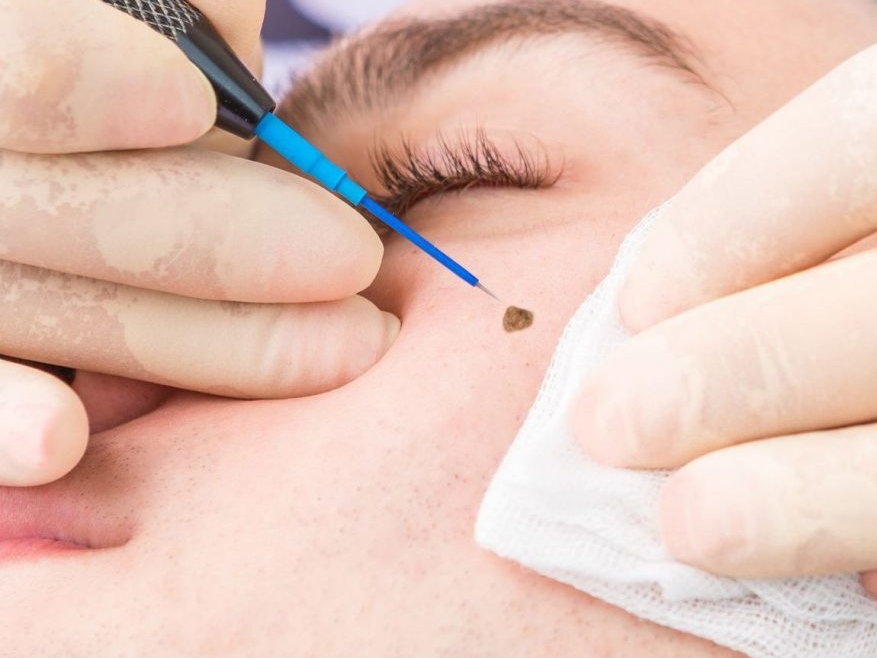
Electrosurgery in dermatology is a widely utilized technique that involves the use of high-frequency electrical currents to cut, coagulate, desiccate, or fulgurate tissue. This method is particularly effective for removing skin lesions, warts, moles, and certain types of skin cancers. Electrosurgery offers precise control over the removal of tissue with minimal blood loss, as the heat generated by the electric current coagulates blood vessels. The procedure can be performed in various modes, such as electrocautery, electrocoagulation, electrodesiccation, and electrofulguration, each tailored to specific clinical needs. For instance, electrocautery involves direct application of a heated electrode to tissues, whereas electrocoagulation uses electric current to induce localized coagulation without significant tissue cutting.
One of the primary advantages of electrosurgery in dermatology is its versatility and efficiency. It allows for rapid treatment of multiple lesions in a single session, often without the need for sutures, which can result in quicker healing and reduced scarring. The precision of electrosurgery minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissue, making it an excellent choice for delicate areas like the face. Additionally, the technique is generally well-tolerated by patients, typically requiring only local anesthesia. However, it is essential for practitioners to be adept in the procedure and aware of potential complications, such as infection or burns, to maximize safety and efficacy. Electrosurgery continues to be a cornerstone in dermatologic treatments, combining effectiveness with patient convenience.